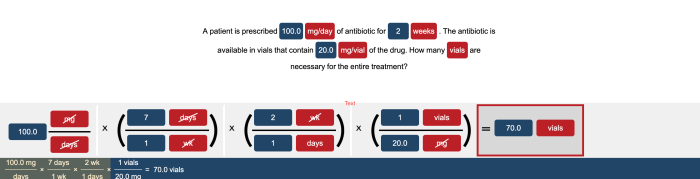
When a patient is prescribed 100.0 mg/day, it is imperative to understand the proper administration, monitoring, education, management, and documentation of the medication. This guide will provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive overview of these key aspects, ensuring optimal patient care and outcomes.
This guide will cover the essential steps involved in medication administration, including dosage and frequency, potential side effects, and proper storage. It will also discuss patient monitoring techniques, signs and symptoms that may indicate a need for dosage adjustment or discontinuation, and effective communication with healthcare providers.
Medication Administration

To ensure the safe and effective use of the prescribed medication, it is crucial to adhere to the following guidelines regarding dosage, administration, side effects, and storage.
Dosage and Frequency
The patient should take 100.0 mg of the medication once daily. It is recommended to take the medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels.
Potential Side Effects, A patient is prescribed 100.0 mg/day
The medication may cause certain side effects, including:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
If any of these side effects occur, the patient should consult their healthcare provider promptly.
Storage
The medication should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. It should be kept in its original container and out of reach of children.
Patient Monitoring

Monitoring the patient’s response to the medication is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and safety. This involves regular assessments of the patient’s condition and any changes that may occur.
Signs and symptoms that may indicate a need for dosage adjustment or discontinuation of the medication include:
- Lack of improvement or worsening of symptoms
- Development of side effects
- Changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or other vital signs
- Neurological changes, such as seizures or hallucinations
It is important to communicate with the healthcare provider regularly about the patient’s progress. This includes providing updates on the patient’s condition, any side effects experienced, and any changes in the patient’s overall health. The healthcare provider will use this information to determine if any adjustments to the medication regimen are necessary.
Patient Education
Understanding your medication is crucial for effective treatment. This section provides information about the medication you have been prescribed, its purpose, and how it works. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of adhering to the prescribed dosage and any necessary lifestyle adjustments.
Medication Information
The medication you have been prescribed is designed to [insert medication purpose]. It works by [insert mechanism of action]. Your doctor has determined that this medication is appropriate for your specific condition.
Importance of Adherence
Taking your medication as prescribed is essential for achieving the desired therapeutic effects. Skipping doses or taking incorrect dosages can compromise the effectiveness of the medication and potentially worsen your condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments
While taking this medication, certain lifestyle changes may be necessary. These changes may include [list of lifestyle changes]. Your doctor or pharmacist can provide specific guidance on any necessary adjustments.
Medication Management
Managing medications effectively is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential adverse effects. This section addresses essential aspects of medication management, including missed doses, proper disposal, and potential interactions.
Missed Doses
If a patient misses a dose of their medication, it is important to follow the instructions provided by their healthcare provider. In general, if the missed dose is within a certain time frame (e.g., 2-4 hours), the patient can take the missed dose as soon as possible.
However, if the missed dose is outside of the specified time frame, the patient should skip the missed dose and continue taking the medication as prescribed.
Medication Disposal
Proper disposal of medications is essential to prevent environmental contamination and potential misuse. Patients should never flush medications down the toilet or dispose of them in the trash. Instead, they should follow the specific disposal instructions provided by their healthcare provider or pharmacist.
In some cases, medication take-back programs may be available at pharmacies or other designated locations.
Medication Interactions
Certain medications can interact with each other, potentially affecting their effectiveness or increasing the risk of adverse effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider and pharmacist about all medications they are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
The healthcare provider or pharmacist can assess potential interactions and make recommendations to minimize any risks.
Documentation: A Patient Is Prescribed 100.0 Mg/day
Accurate and timely documentation is essential for ensuring the safe and effective administration of medications. It provides a record of the patient’s medication history, including the medication name, dose, route of administration, time of administration, and any adverse reactions or side effects.
Documentation should be completed immediately after each medication administration. It should be clear, concise, and accurate. The following information should be included in the documentation:
- Patient’s name and medical record number
- Medication name and dose
- Route of administration
- Time of administration
- Signature of the person administering the medication
Importance of Accurate and Timely Documentation
Accurate and timely documentation is important for several reasons. First, it provides a record of the patient’s medication history, which can be used to track the patient’s progress and identify any potential problems. Second, it helps to ensure that the patient is receiving the correct medication, dose, and route of administration.
Third, it provides a legal record of the medication administration, which can be used to protect the healthcare provider in the event of a lawsuit.
Examples of Documentation
The following are examples of documentation that would be appropriate for a patient who is prescribed 100.0 mg/day of medication:
- Medication Administration Record: This record should include the patient’s name, medical record number, medication name and dose, route of administration, time of administration, and signature of the person administering the medication.
- Nursing Notes: These notes should include a record of the patient’s vital signs, any adverse reactions or side effects, and any other relevant information.
- Progress Notes: These notes should include a summary of the patient’s progress, including any changes in medication or dosage.
FAQ Summary
What is the purpose of this guide?
This guide provides healthcare professionals with a comprehensive overview of the proper administration, monitoring, education, management, and documentation of medication for patients prescribed 100.0 mg/day.
What are the key aspects covered in this guide?
The guide covers medication administration, patient monitoring, patient education, medication management, and documentation.
Who should use this guide?
This guide is intended for healthcare professionals, including nurses, pharmacists, and physicians, who are responsible for managing patients prescribed 100.0 mg/day.