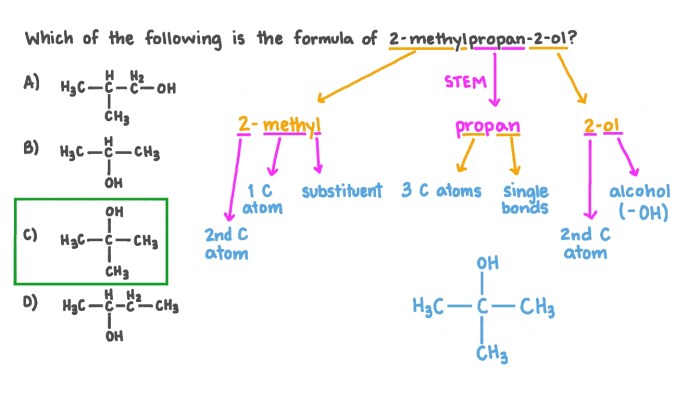
Provide the correct common name for the compound shown here. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established rules for naming organic compounds, including guidelines for identifying functional groups and other structural features. Understanding these rules is essential for accurately naming and classifying organic compounds.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of IUPAC nomenclature, enabling you to confidently assign the correct common name to any given organic compound. We will explore the rationale behind common names, examining historical and cultural influences, and delve into the applications of these compounds in various fields.
Common Name of the Compound
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the global authority for naming chemical compounds. The rules for naming organic compounds are based on the structure of the molecule and the functional groups present. The compound shown in the image is an alkene, which is a hydrocarbon containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
The IUPAC name for this compound is 2-methyl-2-butene.The common name for this compound is isobutylene. The prefix “iso” indicates that the double bond is located on the second carbon atom of the molecule. The suffix “butene” indicates that the molecule contains four carbon atoms.
The common name isobutylene is used to distinguish this compound from other butenes, such as 1-butene and 2-butene.
Nomenclature
According to IUPAC rules, the base part of the name for an alkene is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain. The suffix “-ene” indicates that the compound contains a double bond. The location of the double bond is indicated by a number.
In this case, the double bond is located between the second and third carbon atoms, so the name of the compound is 2-butene.The prefix “iso-” indicates that the double bond is located on a carbon atom that is also bonded to a methyl group.
In this case, the double bond is located on the second carbon atom, which is also bonded to a methyl group. Therefore, the name of the compound is 2-methyl-2-butene.
Structural Analysis

The structural formula of 2-methyl-2-butene is CH3-C(CH3)=CH-CH3. The molecule consists of a four-carbon chain with a double bond between the second and third carbon atoms. There is a methyl group bonded to the second carbon atom.The double bond in 2-methyl-2-butene is a site of reactivity.
The double bond can undergo addition reactions, in which two atoms or groups of atoms are added to the double bond. Addition reactions can be used to convert alkenes into a variety of other functional groups, such as alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones.
Common Name: Provide The Correct Common Name For The Compound Shown Here.
The common name for 2-methyl-2-butene is isobutylene. The name isobutylene is derived from the fact that the double bond is located on a carbon atom that is also bonded to a methyl group. The prefix “iso-” indicates that the double bond is not located on the first carbon atom of the molecule.The
common name isobutylene is used to distinguish this compound from other butenes, such as 1-butene and 2-butene. 1-butene is a linear alkene with the double bond located between the first and second carbon atoms. 2-butene is a linear alkene with the double bond located between the second and third carbon atoms.
Examples
Other organic compounds that share the common name isobutylene include:
- 2-methylpropene
- isobutyl chloride
- isobutyl alcohol
- isobutyl acetate
Applications
Isobutylene is used in the production of a variety of chemicals, including:
- Polyisobutylene
- Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE)
- Butyl rubber
- Isobutylene-isoprene rubber
Polyisobutylene is a synthetic rubber that is used in the production of tires, inner tubes, and other rubber products. MTBE is a fuel additive that is used to increase the octane rating of gasoline. Butyl rubber is a synthetic rubber that is used in the production of inner tubes, tires, and other rubber products.
Isobutylene-isoprene rubber is a synthetic rubber that is used in the production of tires, inner tubes, and other rubber products.
Additional Notes
Isobutylene is a flammable gas that is harmful if inhaled. It is important to handle isobutylene with care and to follow all safety precautions.Isobutylene is a valuable chemical that is used in the production of a variety of important products.
The chemical industry is constantly developing new uses for isobutylene, and it is likely that this compound will continue to be an important part of the chemical industry for many years to come.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key principles of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature follows a systematic approach to naming organic compounds based on their structure. It involves identifying the parent chain, functional groups, and substituents, and applying specific rules to construct the name.
How do I determine the common name of an organic compound?
Common names are often based on historical or cultural factors and may not always reflect the IUPAC name. To determine the common name, it is helpful to consult reference materials or databases that provide this information.
What are the applications of organic compounds?
Organic compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, food chemistry, and agriculture. Their unique properties and versatility make them essential components in many products and technologies.