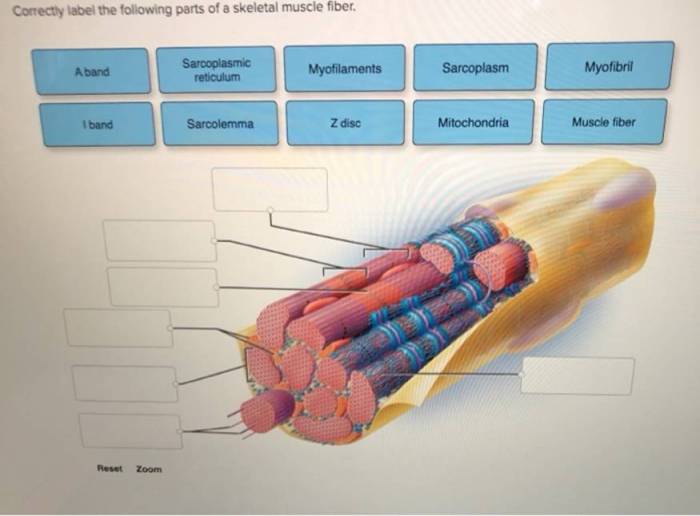
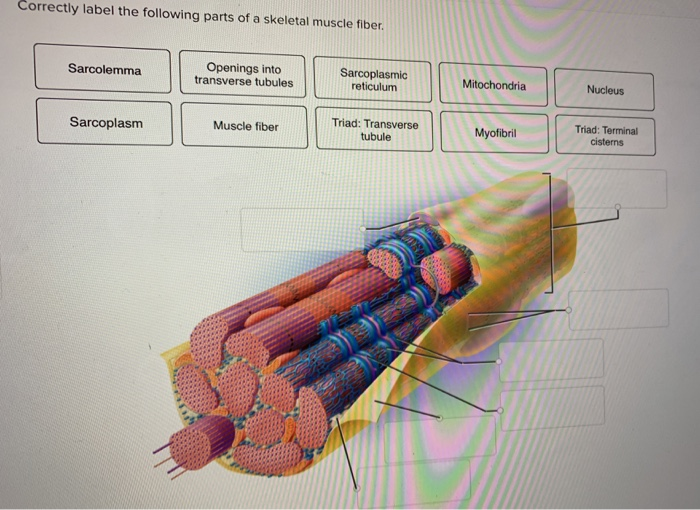
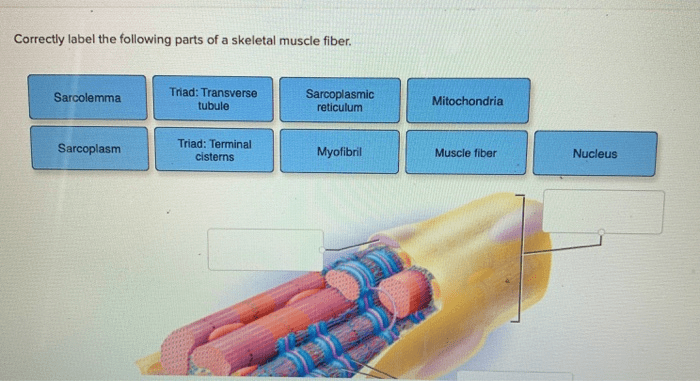
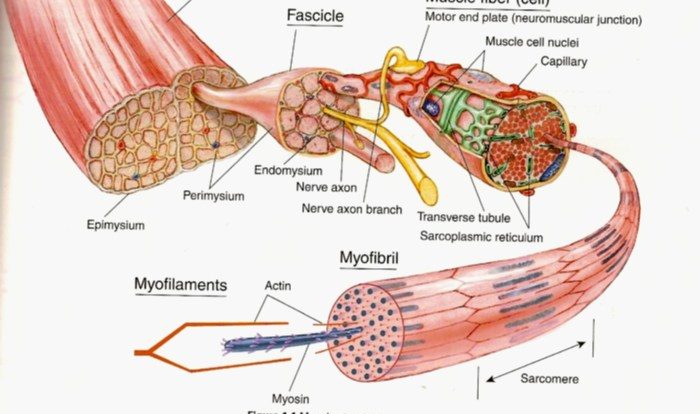
Correctly label the following parts of a skeletal muscle fiber – Correctly labeling the parts of a skeletal muscle fiber is crucial for understanding its structure and function. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key components of a skeletal muscle fiber, their roles, and their organization within the cell.
Skeletal muscle fibers are the basic units of skeletal muscle tissue. They are long, cylindrical cells that contain multiple nuclei and specialized organelles that facilitate muscle contraction and relaxation.
Skeletal Muscle Fiber: Structure and Function: Correctly Label The Following Parts Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber
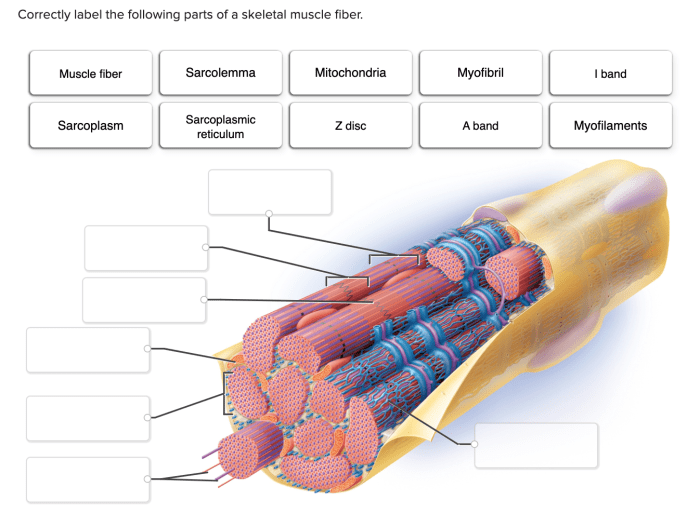
Skeletal muscle fibers are the basic units of skeletal muscle tissue. They are long, cylindrical cells that are responsible for voluntary movement. Each muscle fiber is surrounded by a sarcolemma, which is a thin, plasma membrane that protects the cell and regulates the exchange of substances between the cell and its surroundings.Skeletal
muscle fibers contain several types of organelles, including myofibrils, sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and nuclei. Myofibrils are the contractile elements of the muscle fiber. They are composed of actin and myosin filaments, which slide past each other during muscle contraction. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that surrounds the myofibrils.
It stores calcium ions, which are released during muscle contraction to trigger the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments. Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles of the muscle fiber. They produce ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell.
Nuclei are the control centers of the muscle fiber. They contain the DNA that directs the synthesis of proteins, including the proteins that make up the myofibrils and the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Sarcolemma, Correctly label the following parts of a skeletal muscle fiber
The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of the skeletal muscle fiber. It is a thin, flexible membrane that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The sarcolemma also regulates the exchange of substances between the cell and its surroundings. It contains ion channels that allow the passage of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions.
These ions are essential for muscle contraction.The sarcolemma is also involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. When a nerve impulse reaches the muscle fiber, it causes the sarcolemma to depolarize. This depolarization triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which in turn triggers the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments and muscle contraction.
Myofibrils
Myofibrils are the contractile elements of the skeletal muscle fiber. They are composed of actin and myosin filaments, which are arranged in a repeating pattern called a sarcomere. Sarcomeres are the basic units of muscle contraction.When a muscle fiber is stimulated, the actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, causing the muscle fiber to shorten.
This shortening of the muscle fibers is what produces muscle contraction.The arrangement of the actin and myosin filaments in the sarcomere is essential for muscle contraction. The actin filaments are thin and pointed, while the myosin filaments are thick and blunt.
The myosin filaments have heads that project out from the filament. These heads bind to the actin filaments and pull them toward the center of the sarcomere. This pulling action causes the muscle fiber to shorten.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that surrounds the myofibrils. It stores calcium ions, which are released during muscle contraction to trigger the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments.The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a highly specialized organelle. It is able to rapidly release and re-uptake calcium ions.
This rapid cycling of calcium ions is essential for muscle contraction.The sarcoplasmic reticulum is also involved in the regulation of muscle relaxation. When the muscle fiber is relaxed, the sarcoplasmic reticulum pumps calcium ions back into its lumen. This lowers the concentration of calcium ions in the cytoplasm, which causes the actin and myosin filaments to detach from each other and the muscle fiber to relax.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles of the skeletal muscle fiber. They produce ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell. ATP is used to power the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction.Mitochondria are located throughout the muscle fiber.
They are particularly abundant in the areas where the myofibrils are most active. This ensures that the muscle fiber has a ready supply of ATP to power muscle contraction.Mitochondria are highly efficient at producing ATP. They are able to produce ATP from a variety of substrates, including glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids.
This makes them well-suited to meet the energy demands of skeletal muscle fibers.
Nuclei
Nuclei are the control centers of the skeletal muscle fiber. They contain the DNA that directs the synthesis of proteins, including the proteins that make up the myofibrils and the sarcoplasmic reticulum.Skeletal muscle fibers typically have multiple nuclei. This is because they are formed by the fusion of several smaller muscle cells.
The multiple nuclei ensure that each muscle fiber has a sufficient supply of DNA to direct the synthesis of the proteins that it needs.Nuclei are located throughout the muscle fiber. They are often found in close association with the myofibrils.
This ensures that the nuclei are able to quickly respond to changes in the muscle fiber’s activity and to direct the synthesis of the proteins that are needed for muscle contraction and relaxation.
Essential FAQs
What is the function of the sarcolemma?
The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber. It maintains the integrity of the cell and regulates the passage of substances into and out of the fiber.
What are myofibrils?
Myofibrils are long, thread-like structures within muscle fibers that contain the contractile proteins actin and myosin. They are arranged in a repeating pattern called sarcomeres, which are the basic units of muscle contraction.
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes within muscle fibers that stores calcium ions. When an action potential triggers muscle contraction, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which initiates the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other.