Art-labeling activity anatomy and histology of the thyroid gland – Art-Labeling Activity: Exploring Thyroid Gland Anatomy and Histology introduces a groundbreaking approach to medical education, captivating readers with its innovative use of art as a teaching tool. This engaging activity seamlessly blends the intricacies of anatomy and histology, offering an immersive learning experience that fosters a deeper understanding of the thyroid gland.
Delving into the complexities of the thyroid gland, this activity meticulously describes its gross anatomy, highlighting its location, shape, and size. Microscopic histology takes center stage, unraveling the diverse cell types and their intricate functions within the thyroid gland.
Overview of Art-Labeling Activity
Art-labeling activities involve the use of medical illustrations and require students to label anatomical structures or histological features. These activities are widely used in medical education to enhance understanding and retention of complex anatomical and histological concepts.
The benefits of using art as a teaching tool in anatomy and histology include improved spatial reasoning, enhanced visual memory, and increased engagement. However, challenges may arise, such as the availability of high-quality illustrations and the potential for students to focus on memorization rather than comprehension.
Thyroid Gland Anatomy and Histology
Gross Anatomy
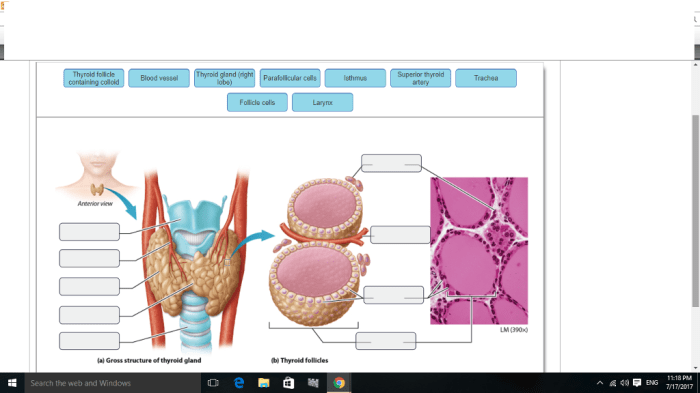
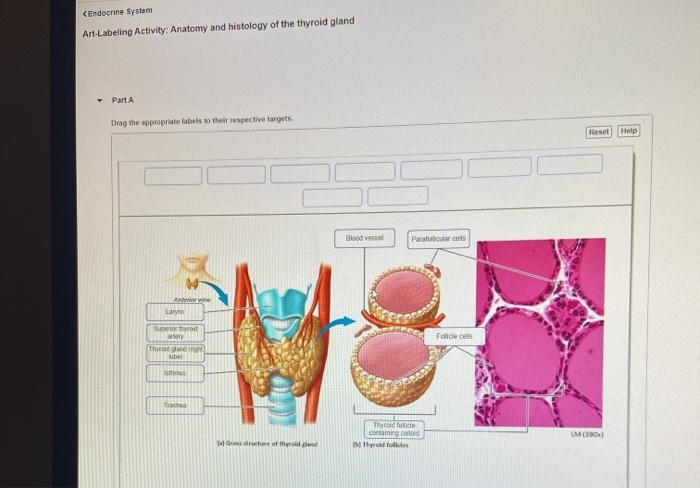
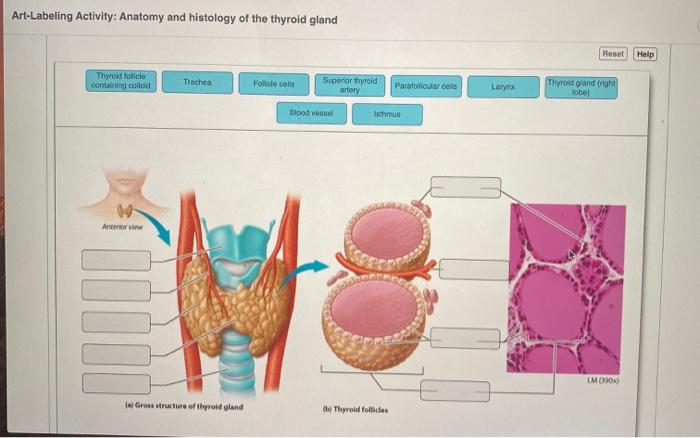
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the anterior neck, inferior to the larynx and cricoid cartilage. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by an isthmus. The lobes are approximately 5 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 2 cm thick.
Microscopic Histology
The thyroid gland is composed of follicles, which are spherical structures lined by a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells. These cells secrete thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which regulate metabolism.
Labeling Techniques and Methods
Various labeling techniques are used in art-labeling activities for anatomy and histology. These include:
- Color-coding:Assigning different colors to specific structures or features.
- Numbers or letters:Labeling structures with numbers or letters that correspond to a key.
- Arrows or lines:Connecting structures or features to their corresponding labels.
- Freehand drawing:Allowing students to draw the labels directly onto the illustration.
The choice of labeling technique depends on the complexity of the illustration and the desired learning outcomes.
Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment of student learning can be conducted through various methods, including:
- Peer review:Students evaluate each other’s labeled illustrations.
- Instructor review:Instructors provide feedback on the accuracy and completeness of student labels.
- Pre- and post-tests:Comparing student knowledge before and after the art-labeling activity.
Providing timely and constructive feedback is crucial for enhancing student learning.
Integration into Curriculum, Art-labeling activity anatomy and histology of the thyroid gland
Art-labeling activities can be integrated into medical education curricula in various ways:
- Standalone activities:Used as independent learning exercises to reinforce concepts.
- Supplementary materials:Accompanying lectures or textbooks to provide visual context.
- Assessment tools:Used to evaluate student understanding and identify areas for improvement.
Alignment with learning objectives and assessment strategies is essential for effective integration.
Educational Resources
Medical educators can access numerous resources to support the implementation of art-labeling activities:
- Online databases:Provide access to high-quality medical illustrations (e.g., Visible Body, Kenhub).
- Tutorials:Offer guidance on labeling techniques and assessment methods.
- Software:Facilitate the creation and sharing of labeled illustrations (e.g., Adobe Illustrator, BioRender).
These resources enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of art-labeling activities.
Q&A: Art-labeling Activity Anatomy And Histology Of The Thyroid Gland
What are the benefits of using art in medical education?
Art fosters visual learning, enhances memory retention, and stimulates creativity, making it an invaluable tool in medical education.
How does art-labeling contribute to understanding thyroid gland anatomy?
Art-labeling allows students to actively engage with anatomical structures and histological features, facilitating a deeper comprehension of the thyroid gland’s intricacies.