Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber and delve into the intricate world of muscle anatomy. From the sarcolemma to the myofilaments, each component plays a vital role in the remarkable ability of skeletal muscles to contract and generate movement.
Unraveling the structural intricacies of skeletal muscle fibers provides a profound understanding of the mechanics of muscle function, paving the way for advancements in fields such as exercise physiology, rehabilitation, and muscle-related disorders.
The Structures of a Skeletal Muscle Fiber: Label The Structures Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber
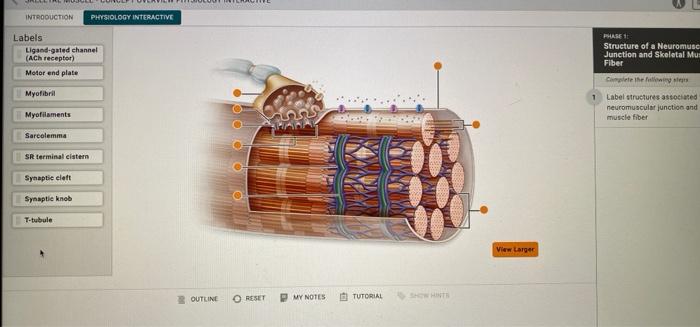
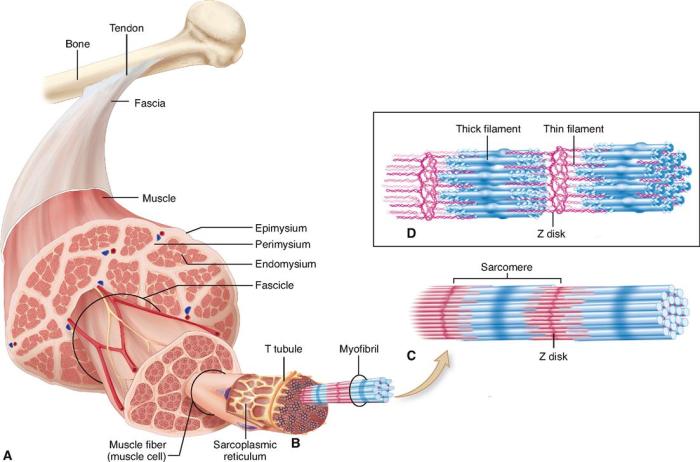
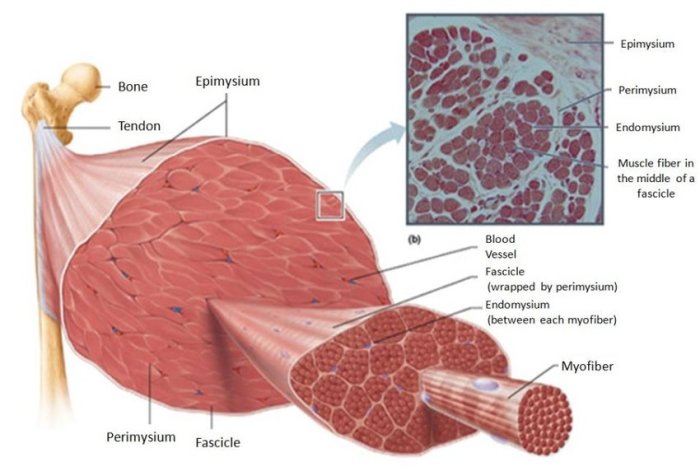
Skeletal muscle fibers are the basic units of contraction in skeletal muscle. They are long, cylindrical cells that contain multiple nuclei and are surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma. The interior of the muscle fiber is filled with myofibrils, which are composed of repeating units called sarcomeres.
These sarcomeres contain the contractile proteins actin and myosin, which are arranged in a specific pattern that allows for muscle contraction.
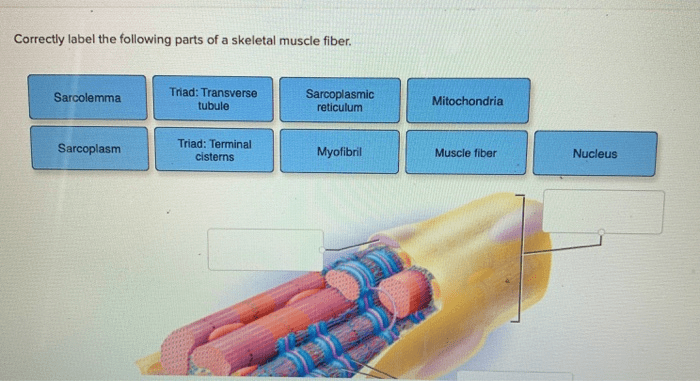
Sarcolemma
The sarcolemma is a thin, flexible membrane that surrounds the muscle fiber. It is responsible for maintaining the integrity of the muscle fiber and for regulating the movement of ions and other molecules across the cell membrane. The sarcolemma also contains receptors for neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that trigger muscle contraction.
Myofibrils
Myofibrils are long, cylindrical structures that run the length of the muscle fiber. They are composed of repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the basic units of muscle contraction. Sarcomeres are composed of actin and myosin filaments, which are arranged in a specific pattern that allows for muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules that runs throughout the muscle fiber. It is responsible for storing calcium ions, which are essential for muscle contraction. When an action potential reaches the muscle fiber, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions into the cytosol, which triggers the contraction of the muscle fiber.
T-Tubules, Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber
T-tubules are small, invaginations of the sarcolemma that run transversely through the muscle fiber. They are responsible for conducting the action potential from the sarcolemma to the interior of the muscle fiber. This allows for the rapid and coordinated contraction of the muscle fiber.
Myofilaments
Myofilaments are the contractile proteins of muscle fibers. They are composed of actin and myosin, which are arranged in a specific pattern that allows for muscle contraction. Actin filaments are thin and contain a binding site for myosin. Myosin filaments are thick and contain a motor domain that interacts with actin filaments to produce force.
Actin Filaments
Actin filaments are thin, flexible filaments that are composed of actin monomers. They contain a binding site for myosin, which is essential for muscle contraction. Actin filaments are arranged in a parallel array within the sarcomere, with the myosin filaments interdigitating between them.
Myosin Filaments
Myosin filaments are thick, rod-shaped filaments that are composed of myosin monomers. They contain a motor domain that interacts with actin filaments to produce force. Myosin filaments are arranged in a parallel array within the sarcomere, with the actin filaments interdigitating between them.
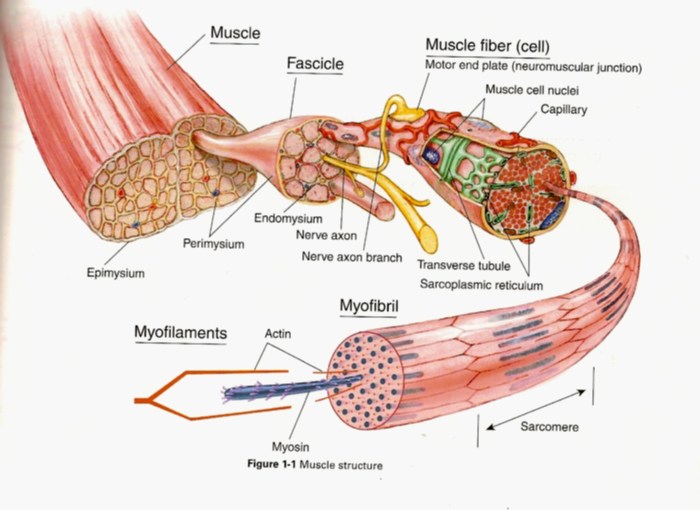
Neuromuscular Junction
The neuromuscular junction is the site where a motor neuron connects to a muscle fiber. It is responsible for transmitting the action potential from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber, which triggers muscle contraction. The neuromuscular junction is composed of a presynaptic terminal, which is located on the motor neuron, and a postsynaptic membrane, which is located on the muscle fiber.
Motor Unit
A motor unit is a group of muscle fibers that are innervated by a single motor neuron. The number of muscle fibers in a motor unit varies depending on the size and function of the muscle. Motor units are responsible for the coordinated contraction of muscle fibers, which allows for the smooth and efficient movement of the body.
Quick FAQs
What is the role of the sarcolemma in muscle contraction?
The sarcolemma plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the muscle fiber and initiating muscle contraction. It transmits electrical impulses from the neuromuscular junction to the interior of the muscle fiber, triggering the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
How do myofibrils contribute to muscle contraction?
Myofibrils are the contractile units of skeletal muscle fibers. They are composed of repeating units called sarcomeres, which contain the myofilaments actin and myosin. During muscle contraction, myosin filaments slide past actin filaments, shortening the sarcomeres and generating force.
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that surrounds the myofibrils. It stores calcium ions and releases them upon stimulation by the sarcolemma. This release of calcium ions triggers the binding of myosin to actin, initiating muscle contraction.