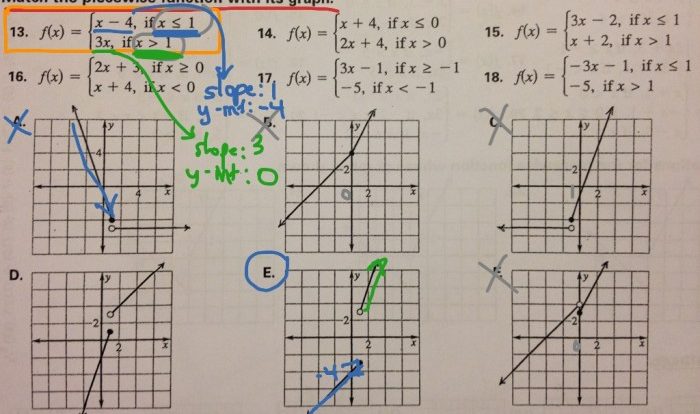The “Multiplying and Dividing Integers Answer Key” provides a comprehensive resource for understanding the fundamental concepts and techniques of integer arithmetic. This guide delves into the intricacies of multiplying and dividing integers, empowering readers with the knowledge and skills to solve complex mathematical problems with accuracy and confidence.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the step-by-step procedures for multiplying and dividing integers, including the application of sign rules. We will also delve into the order of operations, ensuring a clear understanding of the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed.
Real-world examples and practice problems will reinforce the concepts discussed, making this guide an invaluable tool for students and educators alike.
Integer Multiplication: Multiplying And Dividing Integers Answer Key

Integer multiplication involves multiplying two integers, which can be either positive or negative. The sign rules for integer multiplication are as follows:
- Two positive integers multiplied together result in a positive integer.
- Two negative integers multiplied together result in a positive integer.
- A positive integer multiplied by a negative integer results in a negative integer.
- A negative integer multiplied by a positive integer results in a negative integer.
For example:
- 5 x 6 = 30
- -5 x -6 = 30
- 5 x -6 = -30
- -5 x 6 = -30
Integer Division
Integer division involves dividing one integer by another. The sign rules for integer division are as follows:
- Dividing two integers with the same sign (both positive or both negative) results in a positive integer.
- Dividing two integers with different signs (one positive and one negative) results in a negative integer.
For example:
- 12 ÷ 3 = 4
- -12 ÷ 3 = -4
- 12 ÷ -3 = -4
- -12 ÷ -3 = 4
Order of Operations
When multiplying and dividing integers, it is important to follow the order of operations. The order of operations is as follows:
- Parentheses
- Exponents
- Multiplication and Division (from left to right)
- Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)
For example:
- 2 + 3 x 4 = 14
- (2 + 3) x 4 = 20
- 2 3– 5 = 3
- 10 – 2 2= 6
Applications of Integer Multiplication and Division

Integer multiplication and division have a wide range of applications in everyday life, including:
- Calculating area and volume
- Calculating ratios and proportions
- Solving real-world problems
For example, integer multiplication and division can be used to calculate the area of a rectangle, the volume of a cube, or the ratio of two numbers.
Practice Problems
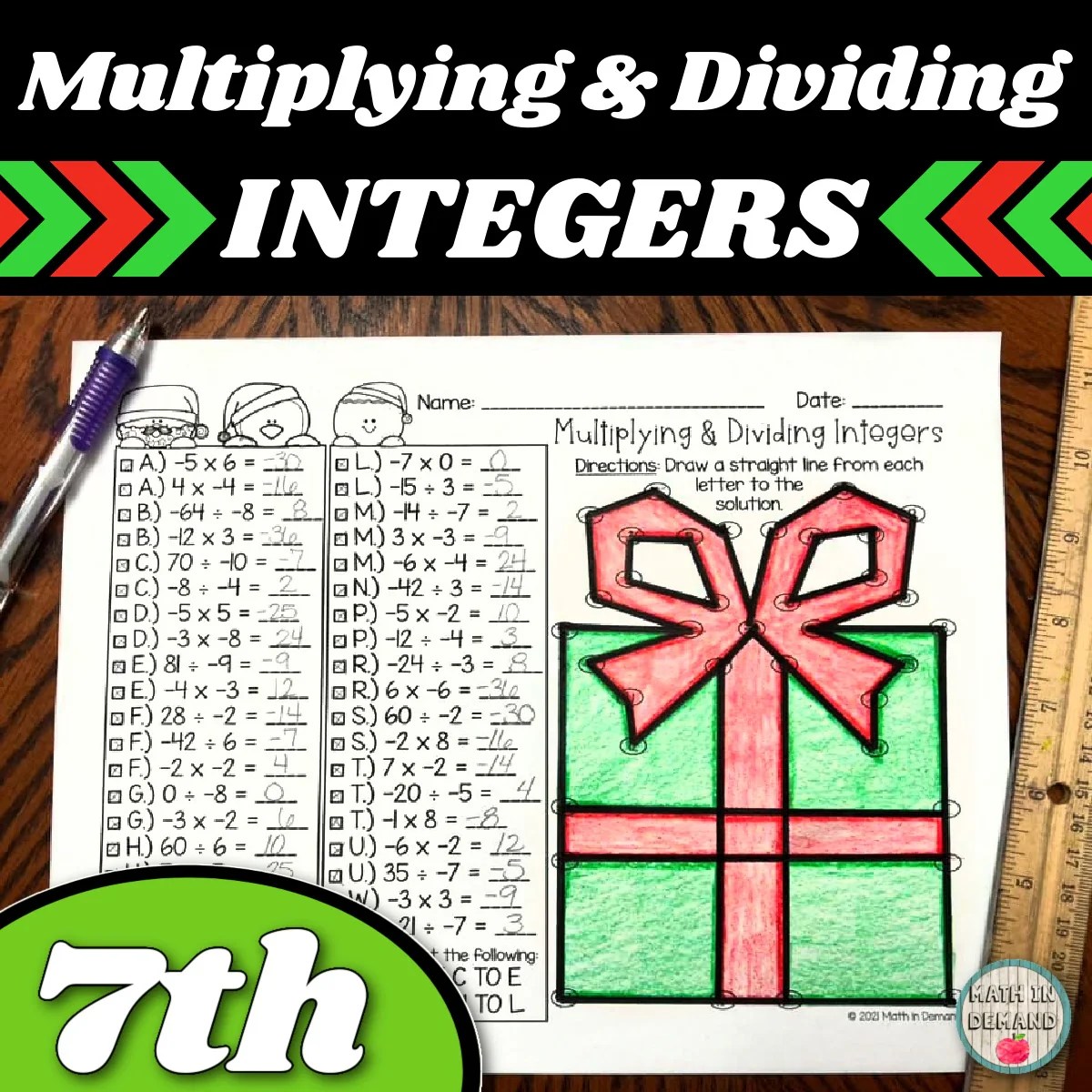
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| 5 x (-6) | -30 |
| -12 ÷ 3 | -4 |
| 2 + 3 x 4 | 14 |
| (2 + 3) x 4 | 20 |
Expert Answers
What is the significance of sign rules in integer multiplication and division?
Sign rules dictate the result of an operation based on the signs of the operands. Understanding these rules is crucial for obtaining accurate answers.
How does the order of operations affect the evaluation of expressions involving integer multiplication and division?
The order of operations (PEMDAS) establishes the sequence in which mathematical operations are performed. Adhering to this order ensures the correct evaluation of expressions.
What are some practical applications of integer multiplication and division in real-world scenarios?
Integer multiplication and division find applications in various fields, including calculating area, volume, ratios, and solving real-world problems involving integers.