Embark on an educational journey with our captivating bones and bone markings quiz! Dive into the fascinating world of osteology, where you’ll uncover the intricate structure and functions of bones, leaving you with a deeper appreciation for these remarkable biological marvels.
Prepare to be amazed as we delve into the complexities of bone anatomy, exploring the diverse types of bone cells, the enigmatic functions of bone marrow, and the comprehensive classification of bone markings. Brace yourself for a thrilling exploration of bone development, remodeling, diseases, and injuries, leaving you with an arsenal of knowledge to conquer any osteological challenge.
Bone Anatomy: Bones And Bone Markings Quiz
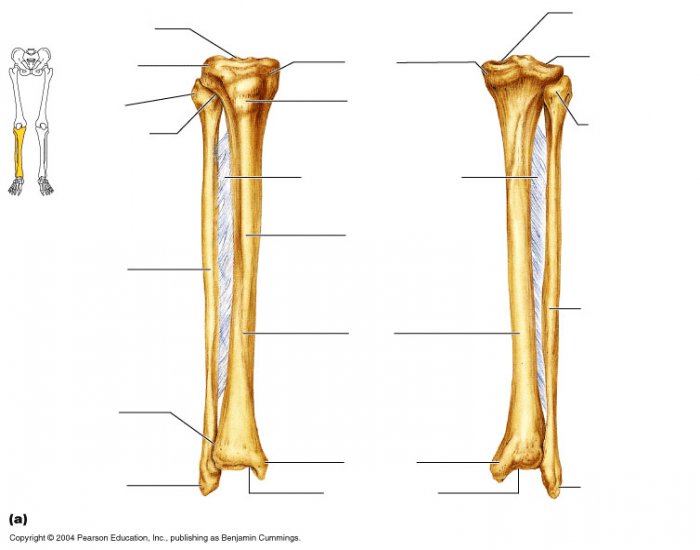
Bones are complex organs that make up the skeletal system, providing support, protection, and movement. They are composed of a hard outer layer called compact bone and a spongy inner layer called cancellous bone. Compact bone provides strength and rigidity, while cancellous bone is lighter and more flexible, allowing for shock absorption and storage of bone marrow.
Bone Cells
- Osteoblasts: These cells are responsible for bone formation by secreting new bone matrix.
- Osteocytes: These are mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue and regulate bone remodeling.
- Osteoclasts: These cells are responsible for bone resorption, breaking down old bone tissue to release calcium and other minerals into the bloodstream.
Functions of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a soft, gelatinous tissue found within the cavities of bones. It has two main functions:
- Hematopoiesis: Bone marrow is the site of blood cell production, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Storage: Bone marrow stores fat, which can be released into the bloodstream as an energy source during times of need.
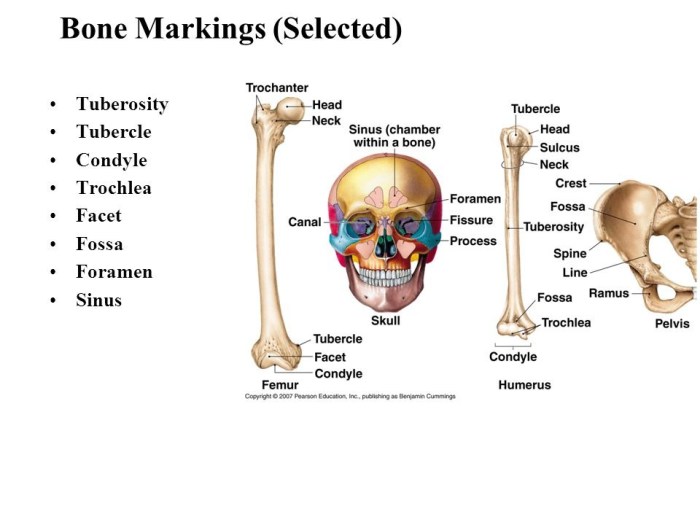
Bone Markings
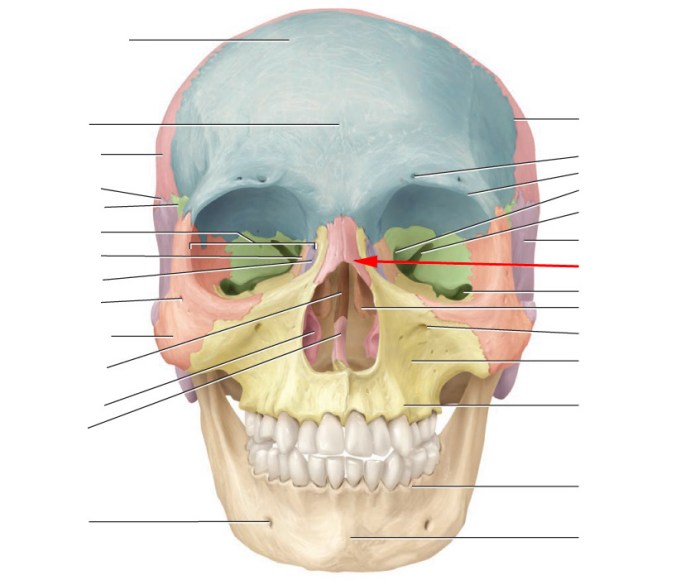
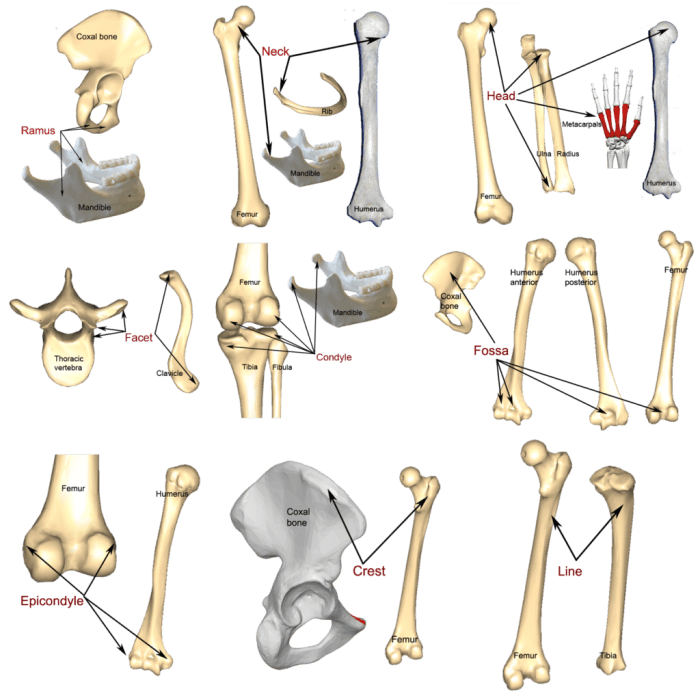
Bone markings are anatomical features that can be found on the surface of bones. These markings provide attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons, and they also serve as passageways for nerves and blood vessels. Bone markings can be classified into several categories, including processes, foramina, fossae, and condyles.
Whether you’re brushing up on your knowledge of bones and bone markings for a quiz or simply curious about the topic, it’s worth considering a different perspective. Is Harrison Bergeron a hero ? This thought-provoking essay explores the complexities of heroism and individuality, offering insights that can enrich your understanding of human nature.
Returning to our study of bones, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of skeletal anatomy.
Processes
Processes are bony projections that extend from the surface of a bone. They can be classified into several types, including:
- Tuberosities: Rounded projections that provide attachment points for muscles.
- Spines: Sharp, pointed projections that provide attachment points for ligaments.
- Trochanters: Large, irregular projections that provide attachment points for muscles.
- Condyles: Smooth, rounded projections that articulate with other bones.
Foramina, Bones and bone markings quiz
Foramina are holes or openings in a bone that allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through. They can be classified into several types, including:
- Nutrient foramina: Small openings that allow blood vessels to enter the bone.
- Emissary foramina: Openings that allow veins to pass from the inside of the skull to the outside.
- Obturator foramen: A large opening in the pelvis that allows nerves and blood vessels to pass through.
Fossae
Fossae are depressions or pits in the surface of a bone. They can be classified into several types, including:
- Articular fossae: Depressions that articulate with other bones.
- Muscle fossae: Depressions that provide attachment points for muscles.
- Nutrient fossae: Depressions that contain nutrient foramina.
The following table summarizes the different types of bone markings, along with their location, function, and examples:
| Type of Bone Marking | Location | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processes | Surface of a bone | Attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons | Tuberosities, spines, trochanters, condyles |
| Foramina | Holes or openings in a bone | Passageways for nerves and blood vessels | Nutrient foramina, emissary foramina, obturator foramen |
| Fossae | Depressions or pits in the surface of a bone | Attachment points for muscles, articulation with other bones, contain nutrient foramina | Articular fossae, muscle fossae, nutrient fossae |
Bone Development
Bone development, or ossification, is a complex process that begins in the womb and continues until early adulthood. It involves the formation of new bone tissue and the remodeling of existing bone.
There are two main types of ossification:
Intramembranous Ossification
Intramembranous ossification occurs when bone tissue forms directly from connective tissue. This type of ossification is responsible for the formation of flat bones, such as the skull and the clavicles.
Endochondral Ossification
Endochondral ossification occurs when bone tissue forms from cartilage. This type of ossification is responsible for the formation of long bones, such as the femur and the humerus.
Bone growth and development are affected by a number of factors, including genetics, nutrition, and exercise.
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process that involves the breakdown of old bone tissue and the formation of new bone tissue. This process is essential for maintaining the strength and integrity of the skeleton, and it occurs throughout life.
Bone remodeling is carried out by two types of cells: osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Osteoblasts are responsible for building new bone tissue, while osteoclasts are responsible for breaking down old bone tissue. The balance between these two cell types determines the overall rate of bone remodeling.
Factors Affecting Bone Remodeling
A number of factors can affect the rate of bone remodeling, including:
- Age: Bone remodeling slows down with age. This is one of the reasons why older adults are more likely to develop osteoporosis, a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle.
- Exercise: Exercise can help to increase the rate of bone remodeling. This is because exercise puts stress on the bones, which stimulates the osteoblasts to build new bone tissue.
- Diet: A diet that is rich in calcium and vitamin D can help to promote bone remodeling. Calcium is essential for the formation of new bone tissue, and vitamin D helps the body to absorb calcium.
Bone Diseases and Injuries
Our bones are living tissues that constantly undergo remodeling to maintain their strength and integrity. However, various diseases and injuries can disrupt this process, leading to bone abnormalities and pain.
Bone Diseases
Bone diseases can arise from genetic defects, hormonal imbalances, or external factors like infections. Some common bone diseases include:
- Osteoporosis:A condition where bones become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures. It primarily affects postmenopausal women and elderly individuals.
- Paget’s Disease:A chronic bone disorder characterized by excessive bone growth and remodeling, leading to deformed and weakened bones.
Bone Injuries
Bone injuries can result from trauma, falls, or repetitive stress. They can be classified into various types:
- Fractures:Breaks in the bone, which can range from hairline cracks to complete breaks. They can be classified as closed (no open wound) or open (bone protrudes through the skin).
- Sprains:Injuries to ligaments, the tough bands of tissue that connect bones. They typically involve overstretching or tearing of the ligaments.
Question Bank
What is the primary function of bone marrow?
Bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What is the difference between intramembranous and endochondral ossification?
Intramembranous ossification involves the direct formation of bone from connective tissue, while endochondral ossification involves the replacement of cartilage with bone.
What are the common symptoms of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis can often be asymptomatic, but common symptoms include bone pain, fractures, and loss of height.